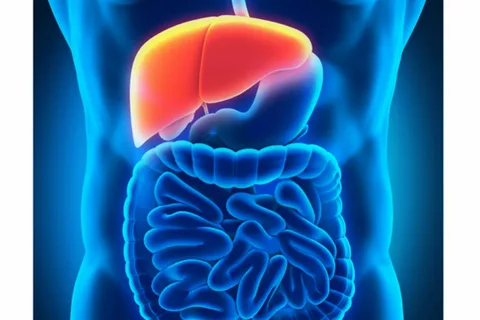
The liver is one of the most important organs in the body, performing a wide range of vital functions, including digestion and detoxification. In this essay, we will discuss the role of the liver in digestion and detoxification and how it supports overall health.
- Digestion –
The liver plays a critical role in the digestion of food. After food is ingested, it is broken down in the stomach and small intestine and then absorbed into the bloodstream. Once in the bloodstream, the nutrients and other substances are transported to the liver for further processing.
- Production of bile – The liver produces bile, a substance that helps digest fats. Bile is stored in the gallbladder and released into the small intestine when needed.
- Regulation of blood sugar – The liver helps regulate blood sugar levels by converting excess glucose into glycogen, which is stored in the liver and muscles. When blood sugar levels are low, the liver converts glycogen back into glucose and releases it into the bloodstream.
- Production of blood proteins – The liver produces a variety of blood proteins, including albumin and clotting factors, which are essential for proper blood clotting and overall health.
- Processing of vitamins and minerals – The liver processes and stores many vitamins and minerals, including vitamins A, D, E, K and B12, as well as iron and copper.
- Detoxification –
The liver is also responsible for detoxification, which is the process of removing toxins and other harmful substances from the body. The liver works in conjunction with other organs, such as the kidneys, to filter out toxins and excrete them from the body.
- Metabolism of drugs and alcohol – The liver metabolizes drugs and alcohol, breaking them down into less harmful substances that can be excreted from the body.
- Removal of toxins – The liver removes toxins from the body, including environmental pollutants, heavy metals and other harmful substances.
- Production of antioxidants – The liver produces antioxidants, such as glutathione, which help protect cells from damage caused by free radicals and other harmful substances.
- Regeneration of liver cells – The liver can regenerate damaged cells, allowing it to recover from injury and continue to function properly.
Overall, the liver plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health by supporting digestion and detoxification. However, certain factors can put a strain on the liver and increase the risk of liver diseases, such as alcohol abuse, viral hepatitis, obesity and exposure to environmental toxins.
- Liver Disease –
Liver disease is a serious condition that can have a significant impact on overall health. There are several types of liver disease, including –
- Cirrhosis – Cirrhosis is a condition in which the liver becomes scarred and damaged, leading to a loss of function.
- Hepatitis – Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver, which can be caused by viral infections, alcohol abuse, or other factors.
- Fatty liver disease – Fatty liver disease occurs when excess fat accumulates in the liver, which can lead to inflammation and scarring.
- Liver cancer – Liver cancer can develop as a result of long-term liver damage, such as from chronic hepatitis or cirrhosis.
Treatment of the liver disease depends on the specific condition and the severity of the damage. In some cases, lifestyle changes, such as quitting alcohol or losing weight, can help reduce the strain on the liver and improve liver function. In more severe cases, medication, surgery or liver transplantation may be necessary.
- Prevention –
Preventing liver disease involves taking steps to reduce the risk of liver damage.
This includes –
- Limiting alcohol consumption – Excessive alcohol consumption can cause liver damage and increase the risk of liver disease.
Getting vaccinated – Vaccines are available to protect against viral hepatitis, which is a major cause of liver disease.
- Maintaining a healthy weight – Obesity and excess body fat can increase the risk of fatty liver disease and other liver conditions.
- Avoiding exposure to toxins – Exposure to environmental toxins, such as pesticides, can increase the risk of liver damage and disease.
- Practicing safe sex – Certain sexually transmitted infections, such as hepatitis B and C, can lead to liver damage and disease.
- Eating a healthy diet – A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help reduce the risk of liver disease.
- Conclusion –
In conclusion, the liver plays a vital role in digestion and detoxification and is essential for overall health. Understanding the functions of the liver and the risk factors for liver disease can help individuals take steps to protect their liver health and prevent liver disease. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including limiting alcohol consumption, avoiding exposure to toxins and eating a healthy diet, can help support liver function and prevent liver disease.