Since the liver and gastrointestinal (GI) systems are intertwined, one’s health can have an impact on the other. This article will examine the relationship between digestive problems and liver health as well as ways to keep both systems in good shape.
Liver and Gastrointestinal System Interaction
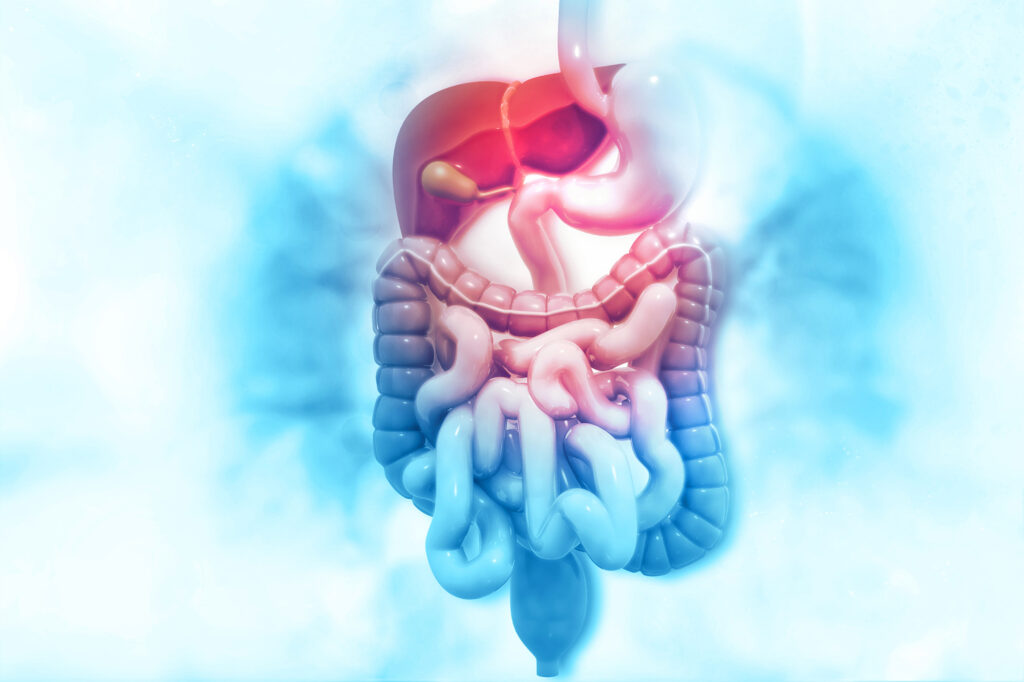
The digestive system is made up of several organs that cooperate to digest food, assimilate nutrients, and remove waste. The liver, the biggest organ in the body, performs a variety of tasks, including removing toxins and making bile to help with digestion. The portal vein, which connects the liver to the digestive system, transports nutrient-rich blood to the liver for processing before it leaves the body.
The Effects of Digestive Disorders on the Liver
The health of the liver can be impacted by some digestive problems, including:
GERD, or Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
A persistent digestive illness called GERD is the source of acid reflux and heartburn. The lining of the esophagus may become irritated and inflamed as a result of stomach acid reflux. GERD can result in Barrett’s esophagus, a disease that raises the risk of esophageal cancer if it is not addressed. According to research, those who have GERD have a higher chance of acquiring liver conditions such as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
IBD, or Inflammatory Bowel Disease
IBD is a collection of long-term diseases that inflame the digestive system. IBD comes in two main forms: Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. IBD can make people more susceptible to autoimmune hepatitis and primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC), two liver conditions.
IBS, or Irritable Bowel Syndrome
The large intestine is affected by the prevalent gastrointestinal illness known as IBS. Constipation, diarrhea, bloating, and stomach discomfort are among the symptoms. Studies have revealed that although IBS does not directly cause liver illness, those who have IBS are more likely to develop liver malfunction.
Celiac Illness
Consuming gluten causes damage to the small intestine’s lining, which is an autoimmune illness known as celiac disease. This harm may eventually make the liver less capable of performing its functions adequately. Celiac disease may occasionally harm the liver and raise the chance of developing liver disease.
GI and Liver Health Can Be Improved by Certain Lifestyle Factors
Consume a Healthy Diet
Both the GI system and the liver benefit greatly from a balanced diet. A diet rich in fibre, fruits, and vegetables helps improve digestion and lessen intestinal inflammation. Antioxidant-rich foods like berries, spinach and almonds can also shield the liver from harm.
Keep Hydrated.
To keep your liver and digestive system healthy, you must consume adequate water. Water assists in digestion and helps the body clean away impurities. Aim to consume eight glasses of water or more each day.
Exercise consistently
Exercise is good for the liver and GI systems. Regular exercise can help with digestion, decrease inflammation, and lessen the chance of developing liver disease. The Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) advise individuals to engage in at least 150 minutes of aerobic exercise of moderate intensity per week.
Reduce your alcohol intake.
Drinking alcohol in excess can harm the liver significantly, thus it’s best to consume it sparingly or not at all. According to the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism, moderate drinking is defined as up to one drink for women and up to two for men per day.
Reduce Stress
The digestive tract and liver function might suffer from stress. Yoga, meditation, and other stress-reduction practice can help lower stress levels and enhance general health.
In conclusion, the liver and gastrointestinal system are closely linked and issues with one can affect the other. Digestive disorders like GERD, IBD, IBS and celiac disease can impact liver health, leading to various liver diseases. However, adopting a healthy lifestyle that includes a balanced diet, regular exercise, stress management and reducing alcohol intake and smoking can improve both GI and liver health. Seeking medical advice promptly if experiencing gastrointestinal symptoms or suspecting liver problems is crucial to prevent further complications and promote overall health and well-being.