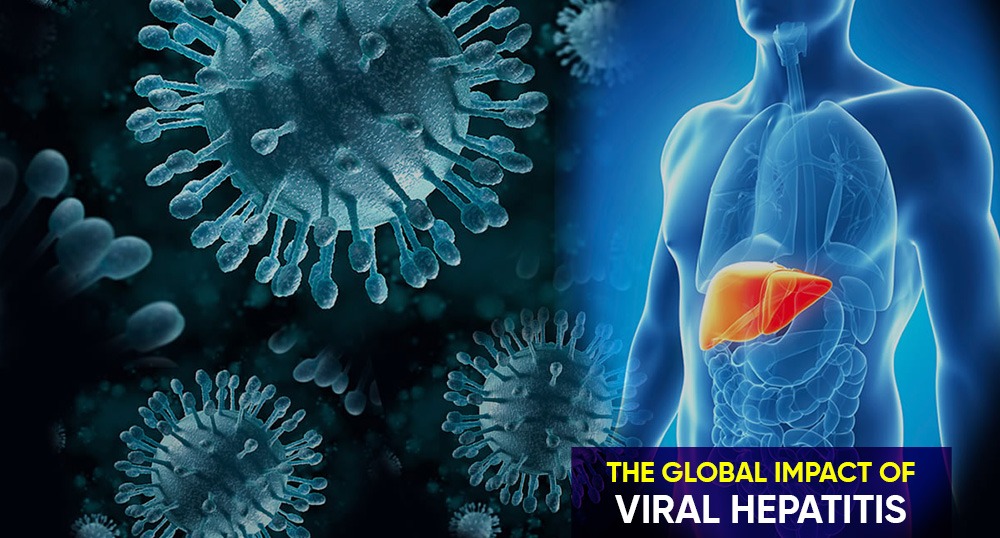
Viral hepatitis is a global health issue that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a group of viral infections that cause inflammation of the liver, and if left untreated, can lead to serious health complications. In this article, we will explore the global impact of viral hepatitis, including its prevalence, causes, symptoms, and treatments.
1). Prevalence of Viral Hepatitis
Viral hepatitis is a significant global health issue, with an estimated 325 million people worldwide living with chronic hepatitis infections. There are five main types of viral hepatitis, including hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E, each caused by a different virus. Hepatitis B and C are the most common and most serious types, responsible for an estimated 96% of hepatitis-related deaths.
2). Causes of Viral Hepatitis
Viral hepatitis is caused by infection with a virus that affects the liver. Hepatitis A and E are typically spread through contaminated food or water, while hepatitis B, C, and D are typically spread through blood or body fluids. The risk of infection is higher for people who inject drugs, have unprotected sex, or are exposed to infected blood or body fluids in healthcare settings.
3). Symptoms of Viral Hepatitis
The symptoms of viral hepatitis can vary depending on the type of virus and the severity of the infection. In some cases, people may not experience any symptoms, while in other cases, they may experience flu-like symptoms such as fatigue, fever, nausea, and abdominal pain. Jaundice, a yellowing of the skin and eyes, is also a common symptom of hepatitis.
Chronic hepatitis infections can lead to serious health complications, such as liver cirrhosis, liver cancer, and liver failure. These complications can be life-threatening, and it is essential to seek medical treatment if you experience any symptoms of viral hepatitis.
4). Treatment for Viral Hepatitis
Treatment for viral hepatitis varies depending on the type of virus and the severity of the infection. Hepatitis A and E infections typically resolve on their own, and treatment focuses on relieving symptoms and preventing dehydration. Hepatitis B, C, and D infections may require antiviral medications to reduce the amount of virus in the body and prevent liver damage.
In some cases, people with chronic hepatitis infections may require liver transplants to replace a damaged liver. Prevention is also essential in reducing the global impact of viral hepatitis. Vaccines are available for hepatitis A and B and can help prevent infection. Safe sex practices, using clean needles, and avoiding sharing personal care items like razors or toothbrushes can also help reduce the risk of infection.
Global Impact of Viral Hepatitis
Viral hepatitis has a significant impact on global health, with an estimated 1.4 million deaths per year attributed to the disease. It is a leading cause of liver cancer and is responsible for over 80% of cases worldwide. The economic burden of viral hepatitis is also significant, with an estimated $6 billion spent annually on hepatitis-related healthcare costs.
Despite the high prevalence and significant impact of viral hepatitis, many people living with the disease are unaware of their infection status. Lack of awareness, stigma and inadequate access to healthcare are significant barriers to prevention and treatment.
In conclusion, viral hepatitis is a global health issue that affects millions of people worldwide. The prevalence, causes, symptoms, and treatments for viral hepatitis vary depending on the type of virus and the severity of the infection. Prevention through vaccines, safe sex practices, and avoiding sharing personal care items is essential in reducing the global impact of viral hepatitis. Increased awareness, reduced stigma, and improved access to healthcare can also help improve prevention and treatment efforts.