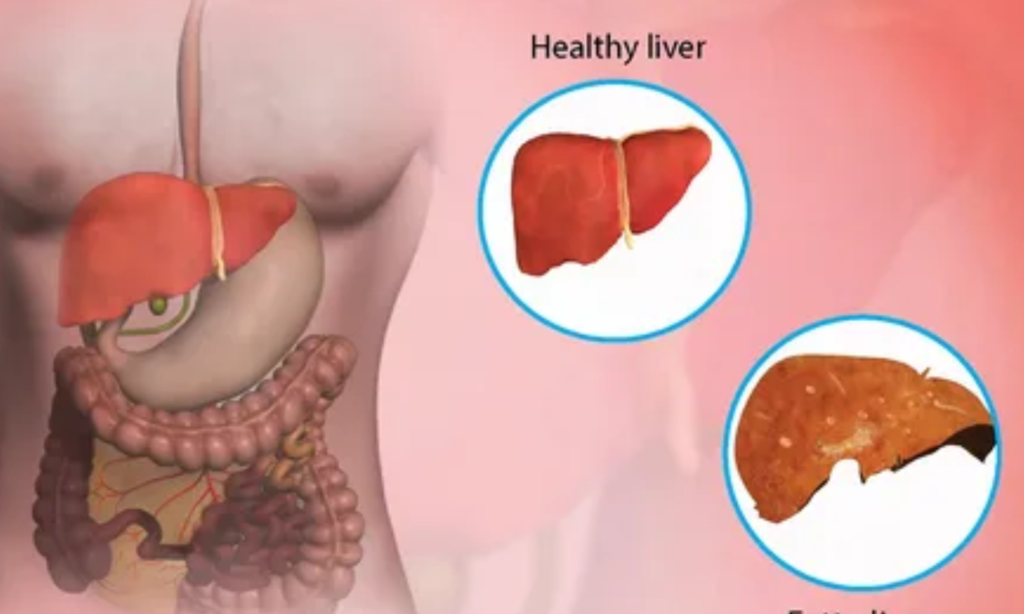
Fatty liver disease, also termed hepatic steatosis, refers to a condition marked by the buildup of fat within liver cells. This condition can range from mild to severe and is often associated with lifestyle factors and underlying medical conditions. Understanding the causes of fatty liver disease is essential for its prevention and management. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the various factors that contribute to fatty liver disease.
1. Alcohol Consumption:
Excessive alcohol consumption stands out as a primary cause of fatty liver disease. Alcohol is metabolized in the liver, and chronic alcohol intake can lead to the accumulation of fat, inflammation, and liver damage. Alcoholic fatty liver disease can progress to more severe conditions such as alcoholic hepatitis and cirrhosis if left untreated.
2. Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome:
Obesity and metabolic syndrome stand out as substantial risk factors linked to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Metabolic syndrome includes conditions such as obesity, high blood pressure, elevated blood sugar levels, and abnormal cholesterol levels. Excess body weight, especially abdominal obesity, contributes to insulin resistance and fat accumulation in the liver, leading to NAFLD.
3. Insulin Resistance and Diabetes:
Insulin resistance, a condition where cells become less responsive to insulin, is closely linked to fatty liver disease. When cells are resistant to insulin, the body produces more insulin to maintain normal blood sugar levels. Elevated insulin levels promote fat storage in the liver, contributing to NAFLD. Diabetes, particularly type 2 diabetes, is often associated with insulin resistance and an increased risk of fatty liver disease.
4. High Dietary Fat and Sugar Intake:
A diet high in saturated fats, trans fats, and added sugars can contribute to fatty liver disease. These dietary components can lead to increased triglyceride levels in the blood, which are then deposited in the liver. Consuming excessive amounts of sugary beverages, processed foods, and fried foods can exacerbate liver fat accumulation and inflammation.
5. Medications and Toxins:
Certain medications and toxins can also cause fatty liver disease. Examples include corticosteroids, methotrexate, tamoxifen, and some antiviral medications. Additionally, exposure to toxins such as pesticides, industrial chemicals, and heavy metals can damage liver cells and contribute to fatty liver disease.
6. Rapid Weight Loss and Malnutrition:
Rapid weight loss, especially through crash diets or bariatric surgery, can lead to the development of fatty liver disease. When the body breaks down fat stores rapidly, the liver may struggle to process the excess fatty acids, leading to fatty liver. Similarly, malnutrition and inadequate protein intake can impair liver function and contribute to liver fat accumulation.
7. Genetics and Family History:
Genetic factors and family history play a role in determining an individual’s susceptibility to fatty liver disease. Some people may have genetic variations that make them more prone to developing NAFLD or alcoholic fatty liver disease, even with relatively modest alcohol consumption or body weight.
8. Other Medical Conditions:
Certain medical conditions can increase the risk of fatty liver disease. These include viral hepatitis (such as hepatitis C), autoimmune liver diseases, Wilson’s disease, and certain inherited metabolic disorders. Managing these underlying conditions is essential in preventing liver damage and complications associated with fatty liver disease.
Summary
Fatty liver disease can have multiple causes, ranging from lifestyle factors such as alcohol consumption, obesity, and high dietary fat intake to medical conditions like insulin resistance, diabetes, and genetic predispositions. Understanding these causes is crucial for early detection, prevention, and effective management of fatty liver disease. If you experience symptoms or risk factors associated with fatty liver disease, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and guidance. Dr. Prasad Bhate, located in Baner, Pune, is the best Gastroenterologist specializing in liver health and can provide personalized care and treatment plans.