Receiving an organ transplant is a life-changing event that requires significant adjustments, especially when it comes to nutrition and lifestyle. Whether you’ve undergone a liver, kidney, heart, or any other organ transplant, proper nutrition plays a crucial role in ensuring the success of the procedure and maintaining your overall health in the long term.
Dietary Restrictions
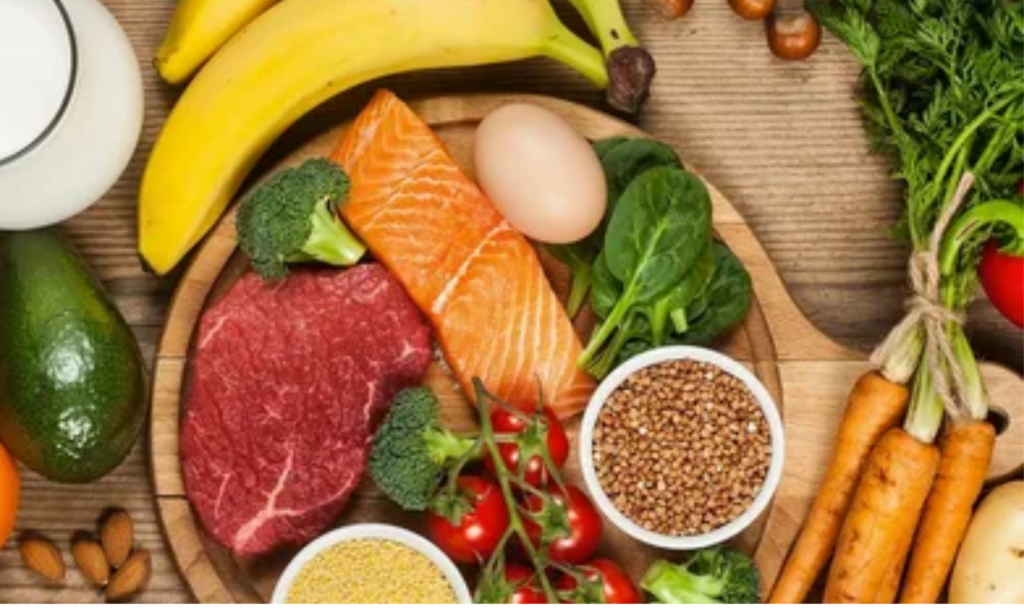
Post-transplant patients often face dietary restrictions aimed at supporting recovery, preventing complications, and maximizing the function of the transplanted organ. Here are some common guidelines:
1. Sodium Intake: Controlling sodium is essential, particularly for heart and kidney transplant recipients, as it helps manage blood pressure and fluid balance. Limiting processed foods, canned goods, and restaurant meals can significantly reduce sodium intake.
2. Fluid Intake: Some transplant recipients may need to monitor fluid intake closely, especially those with kidney transplants. Your healthcare provider will advise on the appropriate amount of fluids based on your individual needs.
3. Protein Needs: Adequate protein intake is crucial for healing and maintaining muscle mass. Lean sources of protein such as chicken, fish, beans, and tofu are generally recommended.
4. Fat Consumption: Choosing healthy fats like those found in avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil supports heart health and overall well-being.
5. Avoiding Certain Foods: Depending on the type of transplant and individual circumstances, certain foods may need to be avoided. For instance, raw or undercooked meats, unpasteurized dairy products, and raw sprouts can pose risks of infection.
Supplements
In addition to dietary restrictions, transplant recipients often benefit from specific supplements to support their health:
1. Vitamin and Mineral Supplements: Some transplant patients may require supplements such as vitamin D, calcium, and iron due to malabsorption or medication effects. Regular blood tests can help determine any deficiencies.
2. Probiotics: These can aid in digestive health, which is often compromised due to medications like immunosuppressants.
3. Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in fish oil supplements, omega-3s help reduce inflammation and support heart health.
4. Multivitamins: A daily multivitamin formulated for transplant patients can help cover essential nutrient needs.
Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle
Beyond dietary considerations, adopting a healthy lifestyle is crucial for overall well-being post-transplant:
1. Exercise: Regular physical activity helps maintain muscle strength, cardiovascular health, and mental well-being. Consult your healthcare team for guidance on suitable exercises based on your condition.
2. Stress Management: Techniques such as meditation, yoga, or counseling can help manage stress, which is beneficial for both physical and mental health.
3. Avoiding Smoking and Alcohol: These habits can interfere with medication effectiveness and overall health, making it essential to abstain post-transplant.
4. Regular Medical Follow-ups: Attend all scheduled appointments with your transplant team for ongoing monitoring and adjustments to your treatment plan.
Summary
Navigating post-transplant nutrition requires attention to detail and adherence to guidelines tailored to your specific situation. Dr. Prasad Bhate, located in Baner, Pune, is the best Gastroenterologist who specializes in post-transplant care. His expertise ensures that patients receive comprehensive guidance on dietary restrictions, supplements, and lifestyle adjustments to optimize their health and recovery.